Packmol Interface¶
Packmol is a tool for creating initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations by packing molecules into a given region of space. molify provides a Python interface to Packmol, making it easy to build molecular systems.
molify ships with a pre-compiled binary of packmol. For more about Packmol, see https://github.com/m3g/Packmol
[1]:
from rdkit.Chem import Draw
import molify
Basic Usage: Creating a Molecular Box¶
The pack() function creates periodic boxes filled with molecules at a specified density.
Simple Example: Water Box¶
[2]:
# Generate water conformers
water = molify.smiles2conformers("O", numConfs=10)
print(f"Generated {len(water)} water conformers")
print(f"Each conformer: {water[0]}")
Generated 10 water conformers
Each conformer: Atoms(symbols='OH2', pbc=False)
[3]:
# Pack 10 water molecules into a box
water_box = molify.pack(
data=[water], # List of conformer lists
counts=[10], # Number of each molecule type
density=1000, # Density in kg/m³
)
print(f"Water box: {water_box}")
print(f"Cell dimensions: {water_box.cell.lengths()} Å")
print(f"Total atoms: {len(water_box)}")
print(f"Volume: {water_box.get_volume():.2f} ų")
Water box: Atoms(symbols='OH2OH2OH2OH2OH2OH2OH2OH2OH2OH2', pbc=True, cell=[6.687972094719516, 6.687972094719516, 6.687972094719516])
Cell dimensions: [6.68797209 6.68797209 6.68797209] Å
Total atoms: 30
Volume: 299.15 ų
The connectivity information from the input Atoms object is preserved in the output box.
[4]:
# Connectivity is preserved!
print(f"Has connectivity: {'connectivity' in water_box.info}")
print(f"Number of bonds: {len(water_box.info['connectivity'])}")
print(f"Expected bonds: {10 * 2} (10 molecules x 2 O-H bonds each)")
Has connectivity: True
Number of bonds: 20
Expected bonds: 20 (10 molecules x 2 O-H bonds each)
Parameters Explained¶
data: List of Conformer Lists¶
data is a list where each element is a list of conformers (ASE Atoms objects) for one molecule type.
data = [
[water_conf1, water_conf2, ...], # Water conformers
[ethanol_conf1, ethanol_conf2, ...] # Ethanol conformers
]
counts: Number of Each Molecule¶
counts=[10, 5] # 10 of first type, 5 of second type
If you need more molecules in the box than created conformers, they will be reused:
water = molify.smiles2conformers("O", numConfs=5)
box = molify.pack(
data=[water],
counts=[10], # Requesting 10 water molecules will use each conformer twice
density=997 # kg/m^3
)
density: Target Density (kg/m³)¶
The box size is automatically calculated to match this density.
Creating Mixtures¶
Water + Ethanol Mixture¶
[5]:
# Generate conformers for both molecule types
water = molify.smiles2conformers("O", numConfs=10)
ethanol = molify.smiles2conformers("CCO", numConfs=10)
print(f"Water conformers: {len(water)}")
print(f"Ethanol conformers: {len(ethanol)}")
Water conformers: 10
Ethanol conformers: 10
[6]:
# Create mixture: 5 water + 5 ethanol
mixture = molify.pack(
data=[water, ethanol],
counts=[5, 5],
density=800, # kg/m³
)
print(f"Mixture: {mixture}")
print(f"Cell: {mixture.cell.lengths()} Å")
print(f"Total atoms: {len(mixture)}")
Mixture: Atoms(symbols='OH2OH2OH2OH2OH2C2OH6C2OH6C2OH6C2OH6C2OH6', pbc=True, cell=[8.728901107040365, 8.728901107040365, 8.728901107040365])
Cell: [8.72890111 8.72890111 8.72890111] Å
Total atoms: 60
Visualizing the Mixture¶
[7]:
# Convert to RDKit for visualization
mixture_mol = molify.ase2rdkit(mixture)
# Visualize
Draw.MolToImage(mixture_mol, size=(600, 400))
[7]:
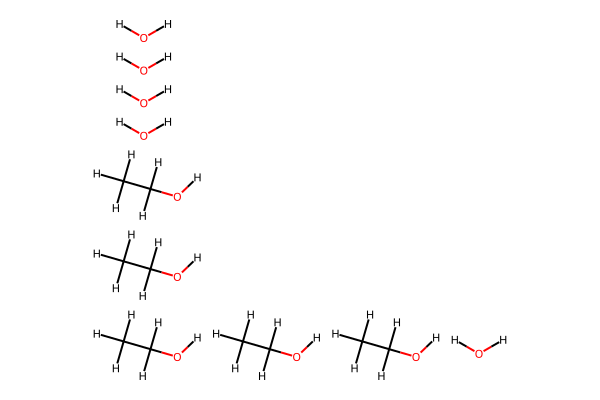
Working with Packed Systems¶
Analyzing the Box¶
[8]:
# Calculate actual density
from molify.utils import calculate_density
actual_density = calculate_density(mixture)
print(f"Density: {actual_density:.1f} kg/m³")
Density: 800.0 kg/m³
Key Takeaways¶
What We Learned¶
pack()creates periodic boxes of molecules at a target density.Only changes atomic positions
Preserves all connectivity information
Preserves bond orders, charges, etc.
Parameters:
data: List of conformer lists (one per molecule type)counts: How many of each moleculedensity: Target density in kg/m³
Conformers are reused if counts > available conformers