ASE Interface¶
The Atomic Simulation Environment (ASE) is a toolkit for atomistic simulations. molify extends ASE by adding chemical connectivity and thereby enabling the integration with rdkit.
For more information about ASE, visit https://wiki.fysik.dtu.dk/ase/
[1]:
import ase.build
from IPython.display import display
import molify
Creating Structures from SMILES¶
molify provides convenient functions to generate ASE Atoms objects directly from SMILES strings.
smiles2atoms(): single 3D structure¶
[2]:
# Create an aldehyde molecule from SMILES with hydrogens.
aldehyde = molify.smiles2atoms("C=O")
print(f"Aldehyde molecule: {aldehyde}")
print(f"Positions:\n{aldehyde.positions}")
print("\nStored information:")
print(f" SMILES: {aldehyde.info['smiles']}")
print(f" Number of bonds: {len(aldehyde.info['connectivity'])}")
Aldehyde molecule: Atoms(symbols='COH2', pbc=False)
Positions:
[[-4.46780196e-02 -1.74057025e-02 7.86262348e-04]
[ 1.17780391e+00 -1.52289849e-01 -1.78379214e-02]
[-3.97811548e-01 1.00725032e+00 1.49697709e-03]
[-7.35314340e-01 -8.37554770e-01 1.55546820e-02]]
Stored information:
SMILES: C=O
Number of bonds: 3
Note: When created from SMILES, the molecule automatically includes:
✅ 3D coordinates (from RDKit’s embedding)
✅ Explicit
connectivityinatoms.info✅ SMILES string in
atoms.info
smiles2conformers(): Multiple 3D Conformers¶
Generate multiple conformers for conformational sampling:
[3]:
# Generate 3 conformers of ethanol
ethanol_conformers = molify.smiles2conformers("CCO", numConfs=3)
print(f"Generated {len(ethanol_conformers)} conformers \n")
for i, conf in enumerate(ethanol_conformers):
print(f" Conformer {i + 1}: {conf}")
Generated 3 conformers
Conformer 1: Atoms(symbols='C2OH6', pbc=False)
Conformer 2: Atoms(symbols='C2OH6', pbc=False)
Conformer 3: Atoms(symbols='C2OH6', pbc=False)
[4]:
# All conformers have the same connectivity
for i, conf in enumerate(ethanol_conformers, 1):
print(f" Conformer {i}: {len(conf.info['connectivity'])} bonds")
Conformer 1: 8 bonds
Conformer 2: 8 bonds
Conformer 3: 8 bonds
ASE → RDKit: The Direct Path (With Connectivity)¶
When ASE Atoms have connectivity information, conversion to RDKit is straightforward:
[ ]:
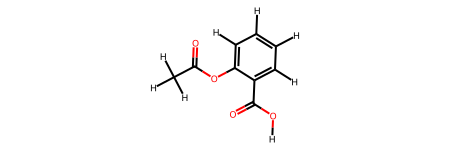
# Create aspirin from SMILES
aspirin = molify.smiles2atoms("CC(=O)Oc1ccccc1C(=O)O")
# Convert to RDKit (exact with existing connectivity data)
aspirin_mol = molify.ase2rdkit(aspirin)
print("Aspirin molecule:")
display(aspirin_mol)
Aspirin molecule:
Internally, ase2rdkit() uses:
ase2networkx()- transfers connectivity to graphnetworkx2rdkit()- converts graph to RDKit molecule
When the full connectivity including the bond_order exists in atoms.info, this conversion does not require any bond guessing.
ASE → NetworkX: Bond Detection from Geometry¶
When atoms.info['connectivity'] is not present, molify will infer bonds from atomic positions using covalent radii when converting ASE Atoms to NetworkX graphs.
Case 1: With Explicit Connectivity¶
[6]:
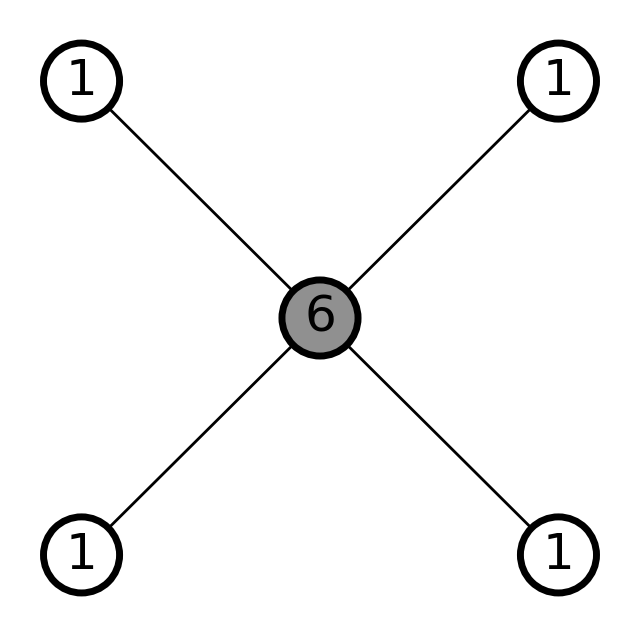
# Create methane with connectivity
methane = molify.smiles2atoms("C")
# Convert to NetworkX - uses explicit connectivity
graph_with_connectivity = molify.ase2networkx(methane)
# Draw the graph using molify's draw_molecular_graph utility
_ = molify.draw_molecular_graph(
graph_with_connectivity,
)
Case 2: Without Connectivity (Bond Detection Required)¶
This example simulates what happens when connectivity information is missing:
[7]:
# Create a molecule and remove connectivity
ammonia = ase.build.molecule("NH3")
print(f"{ammonia.info = }")
ammonia.info = {}
[8]:
# The connectivity is infered from the covalent radii scaled by 1.2
# this method does not determine the type of the bond (bond order).
graph_without_connectivity = molify.ase2networkx(ammonia, scale=1.2)
print(f"Nodes: {graph_without_connectivity.number_of_nodes()}")
print(f"Edges: {graph_without_connectivity.number_of_edges()}")
print("\nEdge attributes (all bonds):")
for u, v, data in graph_without_connectivity.edges(data=True):
print(f" Bond: atom {u} - atom {v}, bond_order = {data['bond_order']}")
Nodes: 4
Edges: 3
Edge attributes (all bonds):
Bond: atom 0 - atom 1, bond_order = None
Bond: atom 0 - atom 2, bond_order = None
Bond: atom 0 - atom 3, bond_order = None
How Bond Detection Works¶
When connectivity is not available, ase2networkx() uses:
Covalent Radii: Each element has a characteristic covalent radius
Scaling Factor: Default
scale=1.2multiplies these radiiDistance Check: Two atoms are bonded if:
distance <= (radius_1 + radius_2) * scale
This includes bonds over periodic boundaries.
Special Handling: Excludes typically non-bonding ions (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr)
The following demonstrates the scale parameter in action:
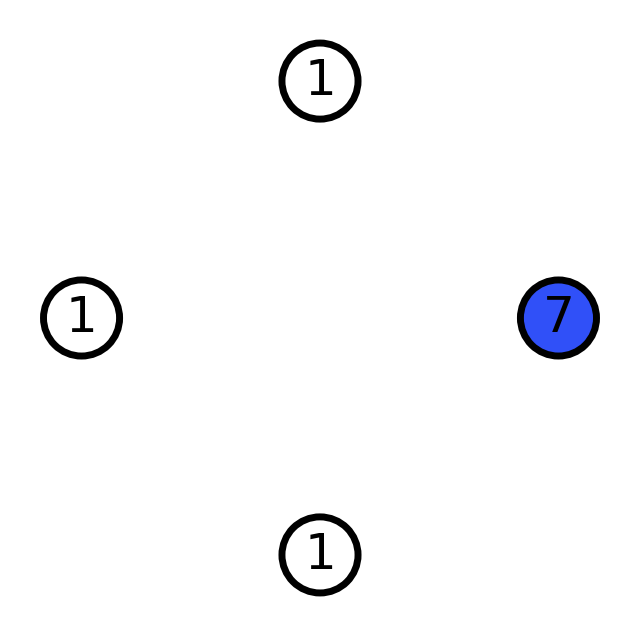
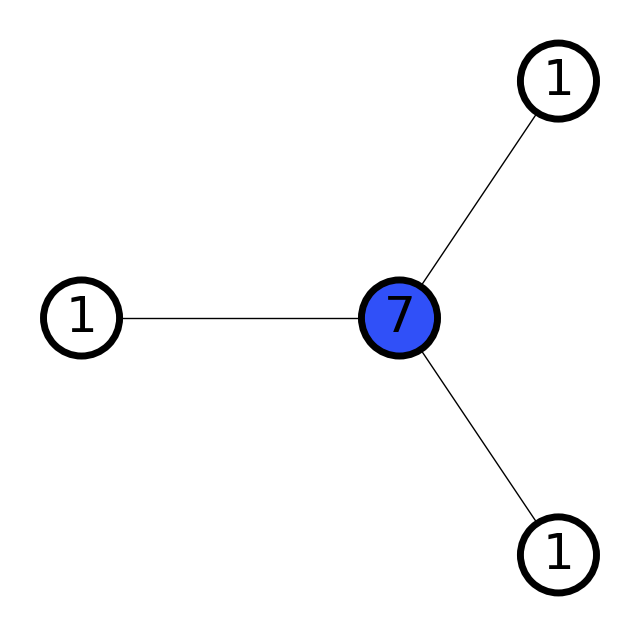
[9]:
# Try different scale values
scales = [0.7, 1.2, 3]
for scale in scales:
graph = molify.ase2networkx(ammonia, scale=scale)
_ = molify.draw_molecular_graph(graph)
print(f"scale={scale}: {graph.number_of_edges()} bonds detected")
scale=0.7: 0 bonds detected
scale=1.2: 3 bonds detected
scale=3: 6 bonds detected
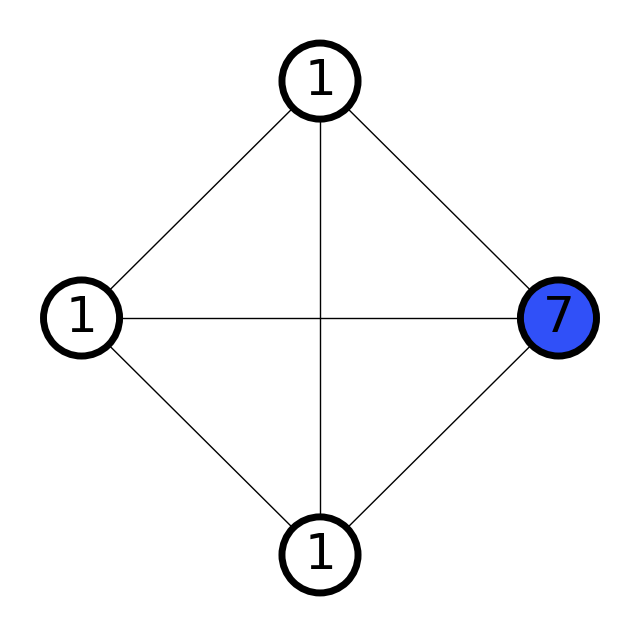
Working with Molecules from Collections¶
Here are some additional examples, based on ASE’s molecule databases. The following converts some of these to RDKit for visualization and analysis:
[10]:
from ase.collections import g2
# Show a few molecules from the G2 database
for idx, (atoms, name) in enumerate(zip(g2, g2.names)):
if idx >= 5: # Show first 5
break
print(f"\n{name}:")
# Note: These molecules don't have connectivity, so we need suggestions
# We'll learn more about this in the NetworkX tools section
mol = molify.ase2rdkit(atoms, suggestions=[])
display(mol)
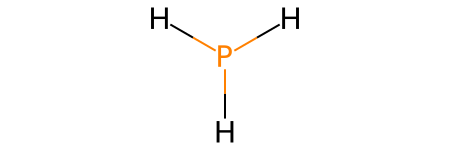
PH3:
P2:

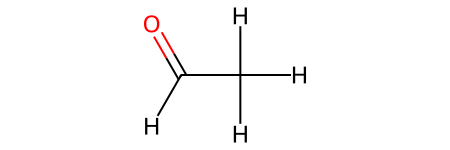
CH3CHO:
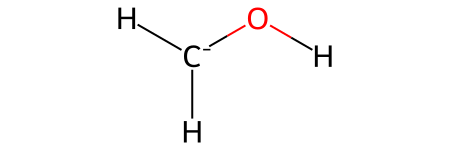
H2COH:
CS:
Key Takeaways¶
What We Learned¶
Creating structures:
smiles2atoms()- single conformer with connectivitysmiles2conformers()- multiple conformersBoth include explicit connectivity information
Bond detection from geometry (when connectivity is missing):
Uses covalent radii ×
scalefactor (default 1.2)Results in
bond_order=Nonein NetworkX edgesatoms.pbcparameter controls periodic boundary handling
Important Concepts¶
bond_order=Nonemeans “bond exists but type is unknown”This happens when inferring bonds from distances